Sales tax compliance has grown increasingly complex, particularly for Shopify merchants. Ensuring compliance with tax regulations can become a burdensome task, diverting attention from the core operations of your online store. However, fear not, for in this blog post, we give an understanding of Shopify sales tax basics, Shopify sales tax collection, as well as challenges and solutions in sales tax compliance, etc. Shopify also provides tools to automatically collect sales tax at checkout, ensuring compliance with various tax regulations. Now, let’s get started!
Understanding Shopify Sales Tax Basics
Before driving the detailed information about Shopify sales tax, we will understand its definition as well as what is sales tax. Sales tax Shopify, a form of consumption tax, is levied by the government on the purchase of goods and services. Typically, it’s paid by the end consumer of a product during the transaction, collected by the seller, and then forwarded to the government at regular intervals, contingent upon factors like the seller’s sales volume, the nature of products, and state regulations.
Sales tax is administered at the state level in 45 states and the District of Columbia. Additionally, certain towns and municipalities may impose local sales taxes. The positive aspect is that businesses are obligated to collect sales tax only if they meet the criteria for establishing a substantial presence in the state, known as the sales tax nexus.
Shopify sales tax represents a small portion of a transaction, directed to governmental entities for certain goods and services sold. Despite the intricate and fluctuating nature of tax laws, Shopify offers the convenience of automating common sales tax calculations.

Understanding Shopify sales tax fees
However, it’s important to note that Shopify does not handle the filing or remittance of sales tax on your behalf. You may need to register your business with local or federal tax authorities to manage your sales tax obligations. The tools and reports provided by Shopify can facilitate the process of filing and paying taxes when the time comes. Additionally, understanding how to charge taxes based on location-based tax settings is crucial for meeting regional tax obligations.
Determining Sales Tax Nexus
Nexus, in the context of sales tax, refers to the connection between a business and a state that triggers a requirement to collect and remit sales tax on transactions occurring within that state. Before 2018, this pertained to a tangible presence, like owning a storage facility. However, following the precedent established in South Dakota v. Wayfair, where the Supreme Court sided with the state's right to impose sales tax on sellers from other states, numerous states have revised their nexus criteria to encompass online sellers lacking physical facilities.

Notice and reporting requirements for unregistered sellers
Consequently, nexus can now be established through either a physical presence or an economic presence within a state.
- Physical presence nexus:
This nexus is established when a business has a tangible presence in a state. It includes in:
- Having a brick-and-mortar store or office in the state
- Owning or leasing property, such as a warehouse or distribution center, in the state
- Employing workers or representatives who conduct business activities within the state
For instance, if an online retailer has a warehouse in California or employs sales representatives who operate in Texas, they would likely have a physical presence nexus in those states and be required to collect and remit sales tax on sales made to customers located there.
- Economic nexus:
It is established based on a business's level of economic activity within a state, regardless of whether it has a physical presence there. This nexus is often triggered by reaching certain thresholds of sales revenue or transaction volume within the state over a specified period.
For instance, Illinois defines economic nexus as reaching either $100,000 in sales or conducting 200 transactions within 12 months. In contrast, Texas establishes an economic presence when sales within the state exceed $500,000 over the previous 12 months.
Shopify Sales Tax Settings (Step-by-Step Guide)
As you know, the sales tax is complicated, as a proprietor of an e-commerce venture, we understand that your plate is full of numerous tasks. Nevertheless, prioritizing the comprehension and effective administration of your sales tax obligations should be paramount. We acknowledge that tax matters, particularly sales tax, can seem intricate, yet accuracy is paramount to adhere to regulations and steer clear of legal entanglements.
Before setting up sales tax collection in Shopify, it is crucial to obtain sales tax permits in states where you have nexus. This ensures you are legally allowed to collect sales tax and comply with state regulations.
So, how to set up Shopify sales tax? Setting up sales tax on your Shopify store doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right approach, you can ensure compliance and streamline the process for both domestic and international sales. In this part, we’ll walk you through the steps to configure sales tax for your US customers and discuss optional considerations for managing international sales tax.
Configuring US Sales Tax in Shopify
As previously stated, each state has its own set of guidelines and standards regarding sales tax thresholds and rates. Follow these steps to set up sales tax collection for your US customers using Shopify sales tax settings:
Step 1: Access Shopify Settings and Taxes Section
Once you’ve completed registration in the states where you have a nexus, it’s time to initiate sales tax collection. If you’re utilizing Shopify, you can commence this process by navigating to Settings > Taxes and Duties> United States.

Access Shopify Settings > Taxes and Duties. United States
For those activating tax collection for the first time, you’ll be prompted to select your preferred tax service: Shopify Tax, Basic Tax, or Manual Tax. Opting for Shopify Tax enables automatic sales tax collection at checkout, utilizing precise rates tailored to products and locations.
Merchants opting for Basic or Manual Tax will need to proceed with additional steps to configure their tax settings. A comprehensive overview of these options can be found in the Shopify Help Center.
Step 2: Enable Sales Tax Collection
Once you’ve chosen your preferred tax section, proceed to select the state where you wish to enable tax collection. Then, navigate to Collecting taxes > Collect sales tax. Tax collection is now activated for that state and will automatically be collected from buyers there.

Navigate to Collecting taxes > Collect sales tax to enable sales tax collection
For sellers operating across multiple channels, it’s essential to collect sales tax from buyers in states where they have a sales tax nexus through each sales channel. If your nexus extends to multiple states, ensure to verify with each platform you sell on to confirm that you’re accurately collecting sales tax from the appropriate buyers.
Step 3: Configure Tax Rates (link to official tax rate resources)
To configure tax rates, you need to identify your product categories in Shopify, you’ll be alerted if certain categories lack products subject to tax collection. If you’ve accurately identified the states where tax collection applies, Shopify will automatically exempt products from tax in those specified regions.
For example, if you’ve designated Pennsylvania for clothing sales, those specific products won’t be taxed. However, if you haven’t specified regions, you’ll need to manually set exemptions or create overrides.
Efficient categorization of products should consider regional tax regulations, reducing the need for overrides. Shopify typically integrates shipping and sales tax collection, applying sales tax to shipping when necessary, and offers options for overrides if required.
Remember, not all products are subject to taxation; for instance, gift cards are usually exempt. State laws differ; in New York, certain clothing items under $110 are exempt from tax.
To configure taxable products, go to “Products“ and select “Add product,” then adjust each variant to specify tax status. Additionally, under “Settings“ > “Locations,” specify warehouse locations to ensure accurate tax rate application based on fulfillment locations.
When you go to edit each variant, make sure to tick the box labeled “Charge tax on this product”:
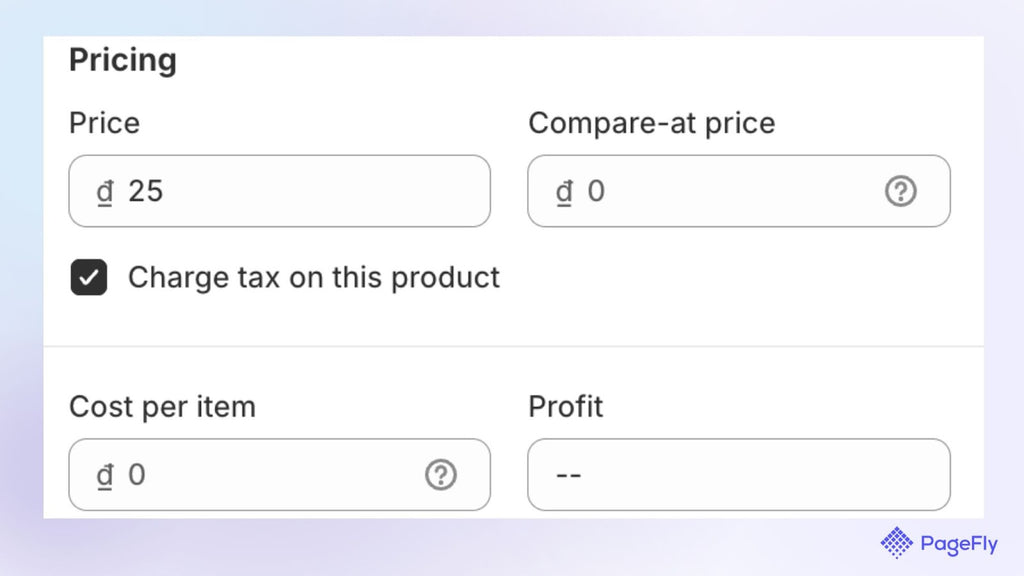
Click “Charge tax on this product” to configure taxable products
Step 4: Set Up Tax Exemptions (if applicable)
The final step, not every customer may necessitate tax collection. Among the common exceptions are resellers who purchase products through your Shopify store for resale, as well as government entities and nonprofits.
Since these transactions are typically recurring, sales tax collection from these specific customers isn’t mandatory. However, you’ll need to obtain a tax-exempt certificate from them beforehand to waive the tax.
To designate these customers as tax-exempt within your Shopify store, navigate to “Customers” and select “Add Customer.”

Navigate to "Customers" and select "Add Customer
Then, ensure that the “Collect tax” option is unchecked, and provide a rationale if needed.

Click the "Collect tax" option unchecked, and provide a rationale if needed for tax-exempt
Managing International Sales Tax (Optional)
As you know, the sales tax will be different in each country; therefore managing international sales tax can be a labyrinthine endeavor due to the diverse tax regulations and compliance requirements across different countries. So, in what point is it different? Here are the complexities of international sales tax
- Variation in tax rates: Different countries have varying tax rates for sales, which can range from value-added taxes (VAT) to goods and services taxes (GST), or even specific sales taxes. These rates may also differ based on the type of product or service being sold.
- Tax jurisdiction: Determining the appropriate tax jurisdiction can be challenging, especially in cases where goods are sold online and can be delivered to customers in multiple countries. Understanding which tax authorities have jurisdiction over a transaction is crucial for compliance.
- Tax exemptions and exclusions: Some countries provide exemptions or exclusions for certain types of transactions or products. Navigating these exemptions requires a thorough understanding of the local tax laws and regulations.
- Registration and filing requirements: Businesses may be required to register for sales tax purposes in each country where they have taxable sales. This involves understanding the registration process, collecting and remitting taxes, and filing periodic tax returns.
- Currency conversion: Dealing with multiple currencies adds another layer of complexity to international sales tax management. Businesses need to accurately convert sales amounts into the local currency to determine the applicable tax liability.
- Compliance challenges: Staying compliant with international sales tax regulations requires ongoing monitoring of changes in tax laws, maintaining accurate records, and implementing robust internal controls to mitigate the risk of non-compliance.
Generating Sales Tax Reports in Shopify
Shopify sales tax report serves as both a compass and a map, guiding you through your sales and tax data breakdown. They categorize information by:
- State
- County
- City
- Time frame
Shopify provides a detailed sales tax report, which helps businesses understand economic thresholds and prepare for tax filing.
These categories provide a thorough record of every tax collection made. Accessing these reports is simple; just navigate to the “Reports” section in your Shopify admin dashboard.

Navigate to the “Reports”section for filing sales tax
Understanding these reports is akin to deciphering a map. You’ll examine detailed summaries of sales and tax data for each order, paying close attention to state, county, and other tax categories. This offers a comprehensive overview of your collected taxes. Similar to how a ship’s log is regularly updated, Shopify’s sales tax reports receive monthly or quarterly updates, aligning with state regulations and your sales volume.
Challenges and Solutions in Sales Tax Compliance
Sales tax compliance can be a daunting task for businesses, especially considering the ever-evolving regulations and complexities involved. Let's explore some of the challenges businesses face in sales tax compliance and effective solutions to address them.

Challenges and Solutions in Sales Tax Compliance
Addressing Complexity and Challenges in Sales Tax Compliance
Sales tax regulations are intricate and constantly evolving, presenting a significant challenge for businesses to navigate. Factors such as varying tax rates, nexus rules, product taxability, and exemptions add layers of complexity to compliance efforts. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has blurred geographical boundaries, further complicating tax obligations for online sellers.
To address these challenges, businesses need to invest in robust tax automation solutions that can adapt to changing regulations and streamline compliance processes. Leveraging cloud-based software equipped with real-time tax calculation capabilities can help businesses accurately calculate and remit sales tax across different jurisdictions.
Leveraging Technology and Expertise to Streamline Sales Tax Management
Technology plays a crucial role in simplifying sales tax management for businesses. Implementing sophisticated tax software not only automates tax calculations but also facilitates reporting and filing processes. You can achieve greater efficiency and accuracy in managing your tax obligations if you integrate tax solutions with existing accounting or e-commerce platforms.
Especially, leveraging expertise in tax compliance is essential for businesses to stay ahead of regulatory changes and optimize their tax strategies.
Proactive Strategies for Mitigating Risks and Ensuring Compliance
In addition to leveraging technology and expertise, adopting proactive strategies is essential for mitigating risks associated with sales tax compliance. Regularly conducting internal audits and reviews can help identify potential issues or discrepancies before they escalate into compliance failures or audit triggers. Implementing robust internal controls and documentation practices can also enhance transparency and accountability in tax reporting processes.

Proactive strategies for Mitigating Risks and Ensuring Compliance (source: unsplash.com)
Shopify Sales Tax FAQ
Calculating sales tax for specific products involves determining the applicable tax rates based on the location of the buyer. Shopify provides tools to automatically calculate taxes based on your store’s settings and the buyer’s address. You can also manually adjust tax rates for individual products if needed.
Whether you need to charge sales tax on shipping costs depends on the tax laws in your jurisdiction. In some areas, shipping costs are taxable, while in others they may be exempt. Shopify allows you to configure tax settings to include or exclude shipping costs from taxable amounts based on your local regulations.
Failure to collect sales tax when required can result in penalties and fines from tax authorities. Additionally, not collecting sales tax could lead to audits and legal consequences for your business. It’s essential to understand and comply with sales tax regulations to avoid these issues and maintain the financial health of your business.
To determine how much sales tax to collect, you can use Shopify's sales tax report. This report helps you identify the amount of sales tax collected from buyers in different states and jurisdictions. By reviewing this report, you can ensure that you are collecting the correct amount of sales tax based on the location of your buyers.











![27 Best Shopify General Stores + Complete Strategy Guide [2025]](http://pagefly.io/cdn/shop/articles/Best_Shopify_General_Stores_2f9d09f2-7c38-4da9-a495-e9f4898ddd68.jpg?v=1757271936&width=1640)





